Want to download this as a PDF? Download now
Natalie Milner, Giulia Poloni, James Reid, Venu Pullabhatla, Lyudmila Georgieva, Graham Speight (Oxford Gene Technology)
Molecular technologies incorporating next-generation sequencing (NGS) are increasingly utilised to support traditional immunophenotypic multiparameter flow cytometry in MRD detection, including acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) disease monitoring.
Real-time qPCR (RT-qPCR) and digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) are highly sensitive technologies but are limited by the number of targets that can be detected in one assay.
NGS offers the opportunity to evaluate many genes in a single assay. Improved accuracy together with falling costs are facilitating the use of NGS in MRD.
We have developed a target-capture NGS approach to support researchers in studies of molecular-based MRD monitoring in myeloid malignancies.
This method provides the opportunity to evaluate many genes and variant types in a single assay.
Libraries were generated using OGT’s Universal NGS Workflow (Fig. 1). The workflow is ideally suited to low frequency variant detection through the inclusion of Unique Dual Indexing (UDIs) and Unique Molecular Identifiers (UMIs).
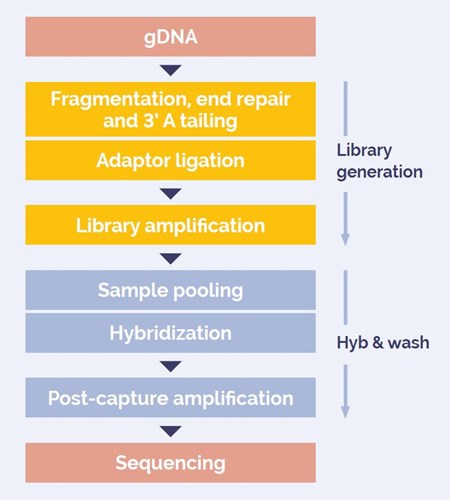
Figure 1: DNA to sequencer in 1 .5 days with minimal handling time.
Myeloid Reference DNA Standard (Horizon Discovery), with 6 SNVs, 2 indels and a 300 bp FLT3 ITD diluted with normal DNA to generate a range of variant allele frequencies (VAFs) between 0.02x - 0.1%.
SureSeq™ Myeloid MRD Panel targeting 43 exons in 13 genes (8 kb target; 11 kb baited).
2 x 150 PE reads, Illumina NextSeq® 500 High Output.
Sequencing data analysis was performed using OGT’s proprietary Interpret software, including read mapping, error correction, coverage calculation and variant calling.
A variant at 0.1% VAF requires a depth of 10,000x to be detected with 10 supporting reads.
A variant at 0.05% VAF requires a depth of 20,000x to be detected with 10 supporting reads.
We increased reads/sample and monitored the depths through:
We used the UMIs for error correction and determined the effect of increased reads on:
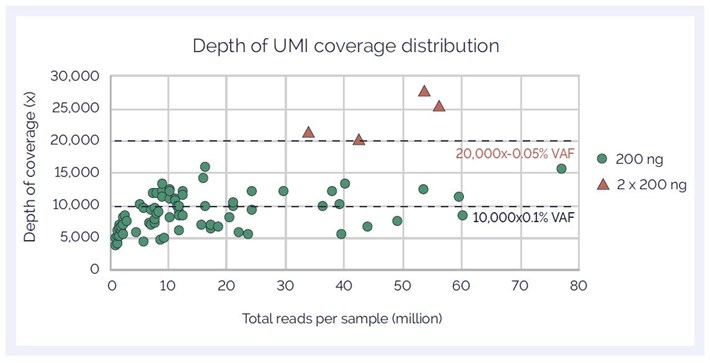
Figure 2: Relationship between sequencing and unique depth of coverage
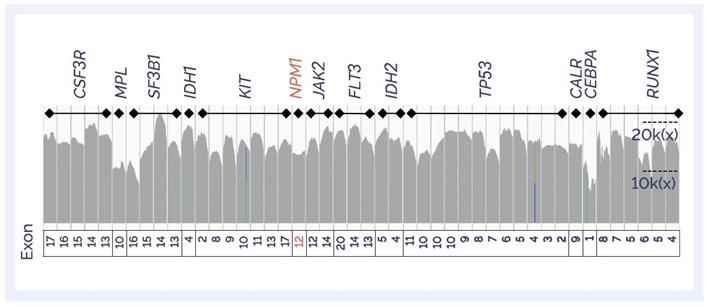
Figure 3: IGV plot showing coverage profile of target regions in the Panel
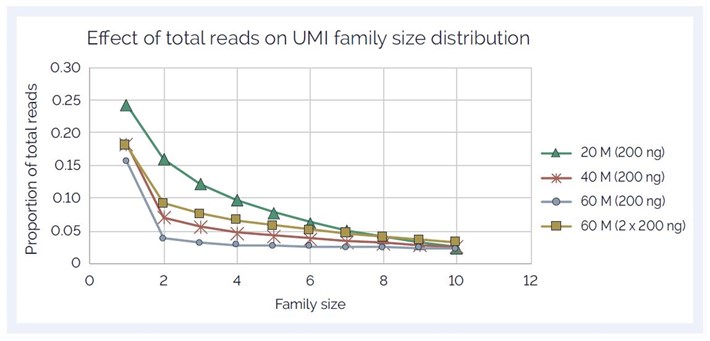
Figure 4: UMI family size (FS) distribution showing increase with increasing reads/sample
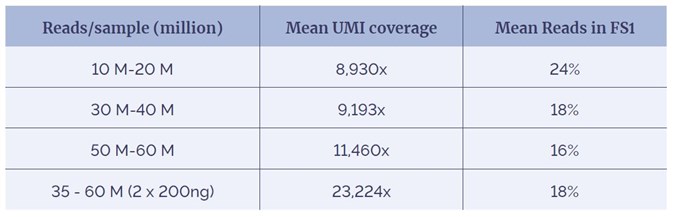
Table 1: Percentage of reads removed in error correction reduces as depth increases.
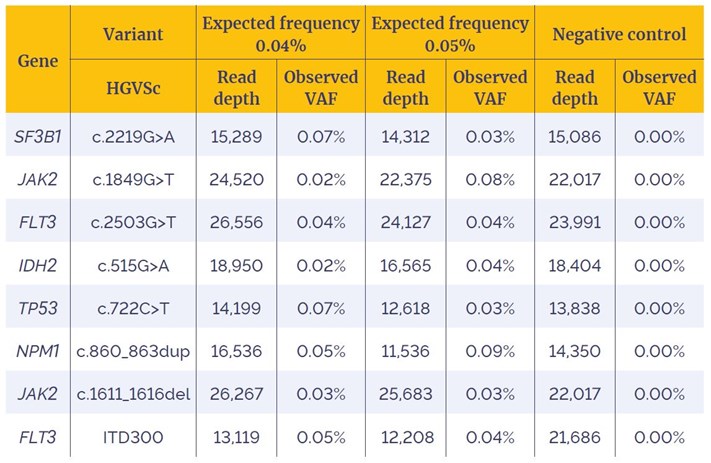
Table 2: Detection of SNVs, Indels and an ITD, with expected frequency ranges of 0.04%-0.05%. SNVs are filtered to remove FS1 reads.
SureSeq: For Research Use Only; Not for Diagnostic Procedures.
