Ruth Burton and Douglas Hurd
Array comparative genomic hybridisation (aCGH) is a well-established technique used to detect chromosomal abnormalities, particularly in conditions such as development delay and intellectual disabilities. To identify potentially disease causative genomic regions, DNA from the test sample is labelled with one fluorescent dye, usually Cyanine 5 and a second reference sample is labelled with a different fluorescent dye, typically Cyanine 3. The two labelled samples are then competitively hybridised to a microarray.
Differences in copy number between the test and reference sample are calculated by measuring the signal intensities of the two dyes and converting these measurements to a ratio. Efficient labelling of both test and reference samples is a critical step in the microarray process and poor labelling can result in inaccurate and potentially misleading data.
This application note provides a technical evaluation of CytoSure® Genomic DNA Labelling Kits compared with another leading DNA labelling kit. CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits are shown to improve key microarray quality control (QC) metrics and consistently generate data with improved signal-to-noise ratios and low derivative log ratio spreads (DLRS).
DLRS is perhaps the most important QC metric and calculates the probe-to-probe log ratio noise of an array. A poor DLRS value means that it is more difficult to accurately call amplification or deletion events. The DLRS is affected by several factors including DNA quality and the labelling reaction. During the labelling reaction all regions of the genome should be labelled equally, the incorporation of the fluorescent nucleotides should be uniform and not affected by local differences in GC content or secondary structure. CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits have been optimised to ensure maximum efficiency and accuracy of the enzyme.
The signal intensity refers to the average raw signal intensity for each channel. This metric is highly dependent on the labelling method used. High signal intensities are desirable and indicate that the labelling reactions have been successful. However, this metric should not be assessed in isolation as the ability to accurately detect aberrations is influenced primarily by the overall signal-to-noise ratio. CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits are designed to incorporate sufficient fluorescent molecules to generate strong signals without generating saturated features.
Background noise is calculated by looking at the negative control features on the array and is a measure of non-specific hybridisation. High background noise values can be caused by incomplete removal of unincorporated dye molecules following the labelling reaction or from technical issues during the washing steps. As with the signal intensity metric, this value should not be considered in isolation and can be linked to high signal intensities. To minimise the background noise, CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits have been carefully optimised to use exactly the right concentration of fluorescent nucleotides, ensuring that the majority of the fluorescent nucleotides are incorporated and not carried over after the clean-up step into the hybridisation reaction.
The signal-to-noise ratio is calculated by dividing the signal intensity by the background noise and indicates how clearly the spots can be detected above the background level. This is a key metric when evaluating the performance of a labelling reaction as it indicates how accurately the spots can be detected. This metric is dependent on the sample labelling, clean-up steps and washing procedures. By achieving high signal intensities without negatively impacting background noise, CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits ensure accurate, reliable detection of even the smallest of aberrations.
CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits are available in two formats: standard and high-throughput. Both kits use the same formulation but the high-throughput protocol has been optimised so that the samples can be processed in a plate rather than in a tube.
The technical performance of both kits is identical, meaning kit selection is based on the number of samples being processed at one time. For laboratories running one or two arrays a week, the standard CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kit is preferable, whereas those laboratories running more than two arrays, particularly the high multiplex 8x format, the CytoSure HT Genomic DNA Labelling Kit would be most efficient. The protocols for both kits have been optimised to ensure fast and simple sample handling with minimal hands-on time (Figure 1). CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits have been developed to work with heat fragmented DNA and so do not require restriction digest of the sample DNA, which saves 1–2 hours compared with typical DNA labelling kits. In addition heat fragmentation is quicker, cheaper and can be performed with no loss of material. Removing the restriction digest stage enables both workflows to easily be completed in a single day. We have also carefully evaluated the purification step, and for the 24 reaction kits have selected columns that are reliable, easy-to-use with purification being achieved in a single spin. This reduces hands-on time and minimises the chance of sample mix-up.
The performance of CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits is carefully monitored. Every batch of reagents is tested and evaluated, and stringent QC checks have to be passed. This ensures that CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits consistently deliver low DRLS (Figure 2).
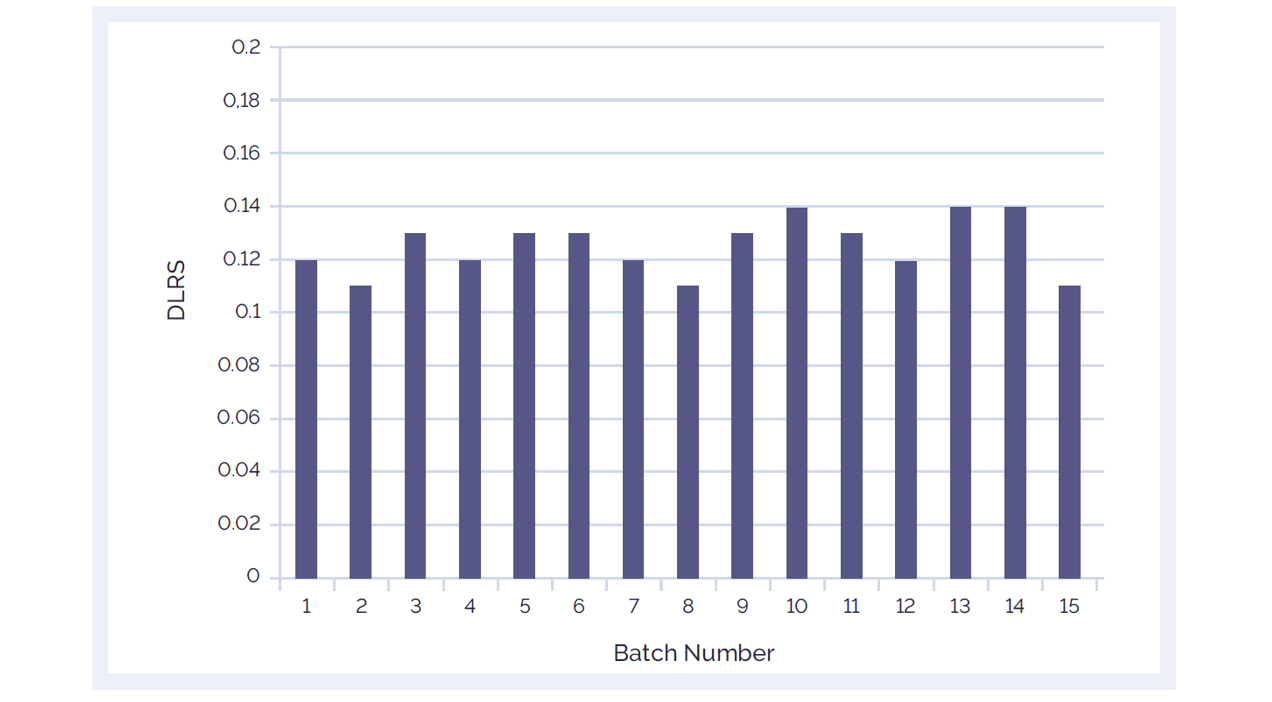
Figure 2: The CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kit delivers consistently low DLRS values ensuring accurate aberration detection. 15 different batches of CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kit reagents were tested using standard reference DNA samples from Promega™ and CytoSure Arrays. The average DLRS value is 0.127.

When choosing a labelling kit, it is important to consider the performance of the kit compared with other commercially available products. Experimental validation at OGT’s laboratories shows that the CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kit delivers significantly lower DRLS than a leading alternative product (Figure 3). A DRLS value below 0.2 is considered excellent; all of the samples labelled with CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kit are below 0.2.
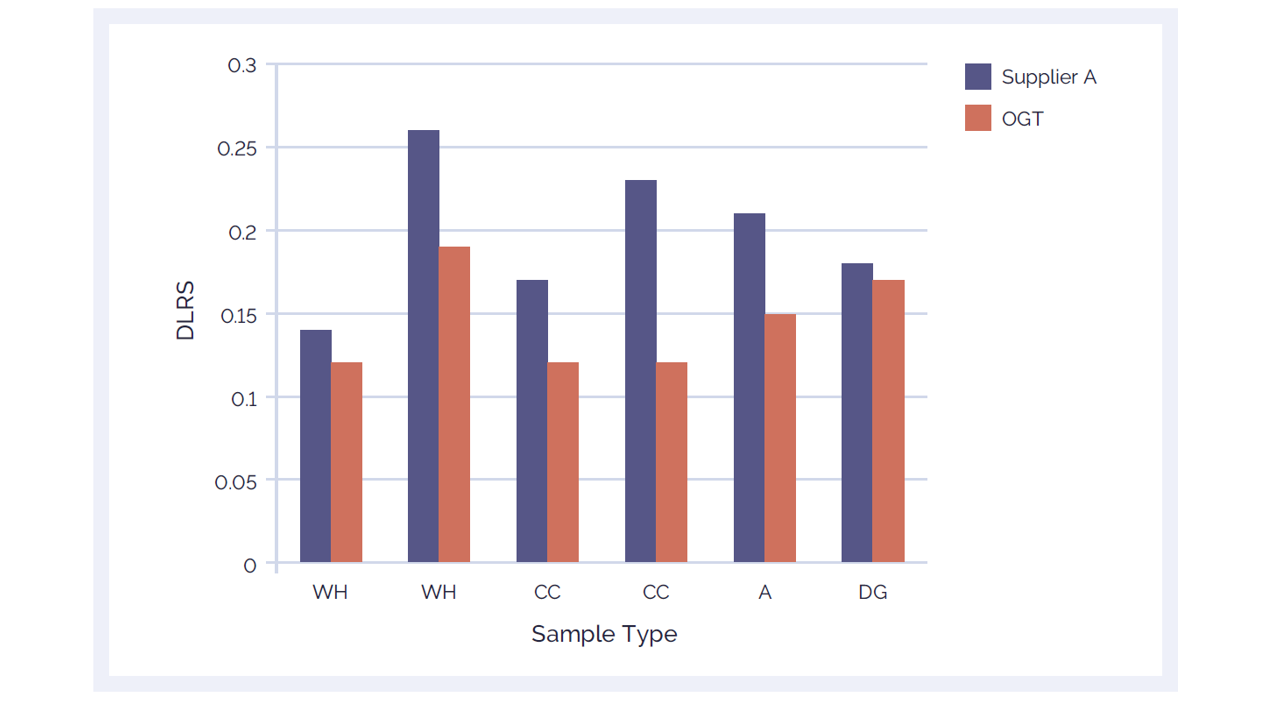
Figure 3: CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits provide lower DLRS than a leading alternative product, ensuring accurate aberration calling. Using the CytoSure ISCA v2 4x180k arrays, the DLRS of 6 sample pairs labelled using the CytoSure Genomic HT DNA Labelling Kit (red bars) are compared against the DLRS obtained using a leading alternative kit (Supplier A) (blue bars). The CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kit delivered consistently lower DRLS values than those obtained from Supplier A. The samples used were commercially available Coriell DNA (WH: WolfHirshhorn; CC: Cri du Chat; A: Anglemans; DG: Di George).

The CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kit also generates microarray data that has a significantly improved signal-to-noise ratio compared to a leading alternative product (Figure 4). For both red and green channels a signal-to-noise ratio above 85 on a 4x180k CytoSure array is considered excellent. All of the samples which had been labelled with CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kit were well above this value. Signal-to-noise ratios in the range 30-85 are considered “good”.
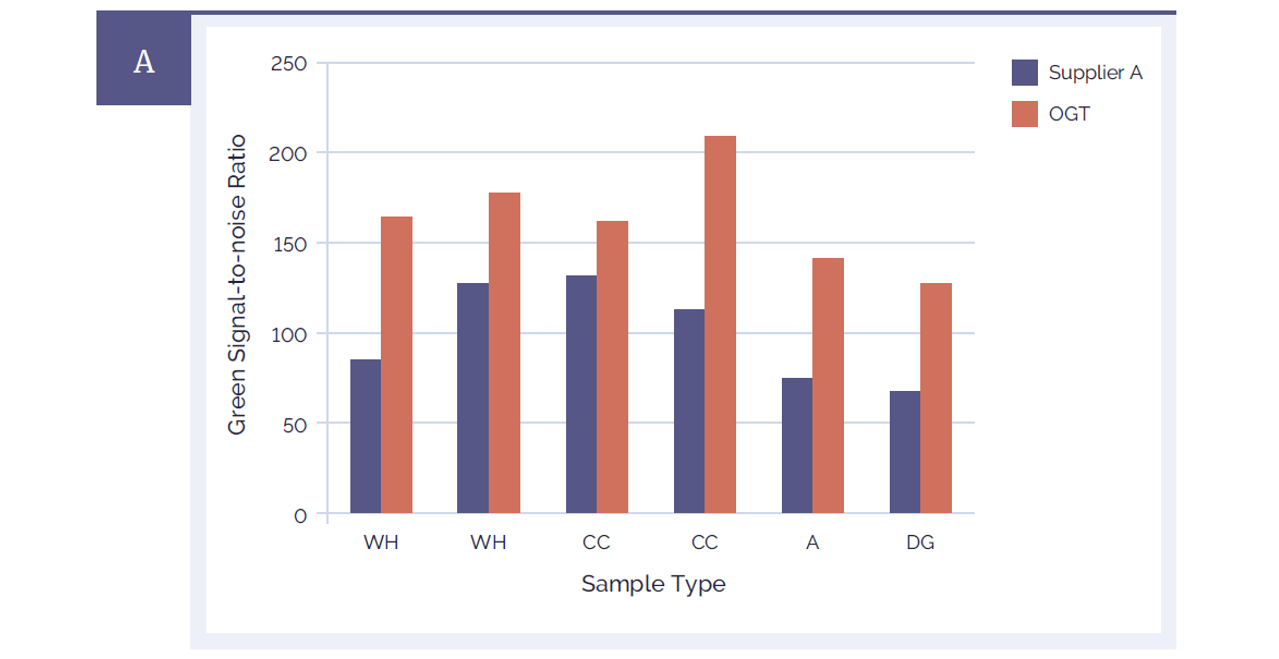
Figure 4A: CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits provide significantly improved signal-to-noise ratios than a leading alternative product. Using CytoSure ISCA v2 4x180k arrays the signal-to-noise ratios of 6 sample pairs labelled using the CytoSure Genomic HT DNA Labelling Kit (red bars) are compared against the signal-to-noise ratios obtained using a leading alternative kit (Supplier A) (blue bars). Panel A illustrates the green channel data, Panel B the red channel data. The CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kit delivered consistently higher signal-to-noise ratios than those obtained from Supplier A. The samples used were commercially available Coriell DNA (WH: WolfHirshhorn; CC: Cri du Chat; A: Anglemans; DG: Di George).

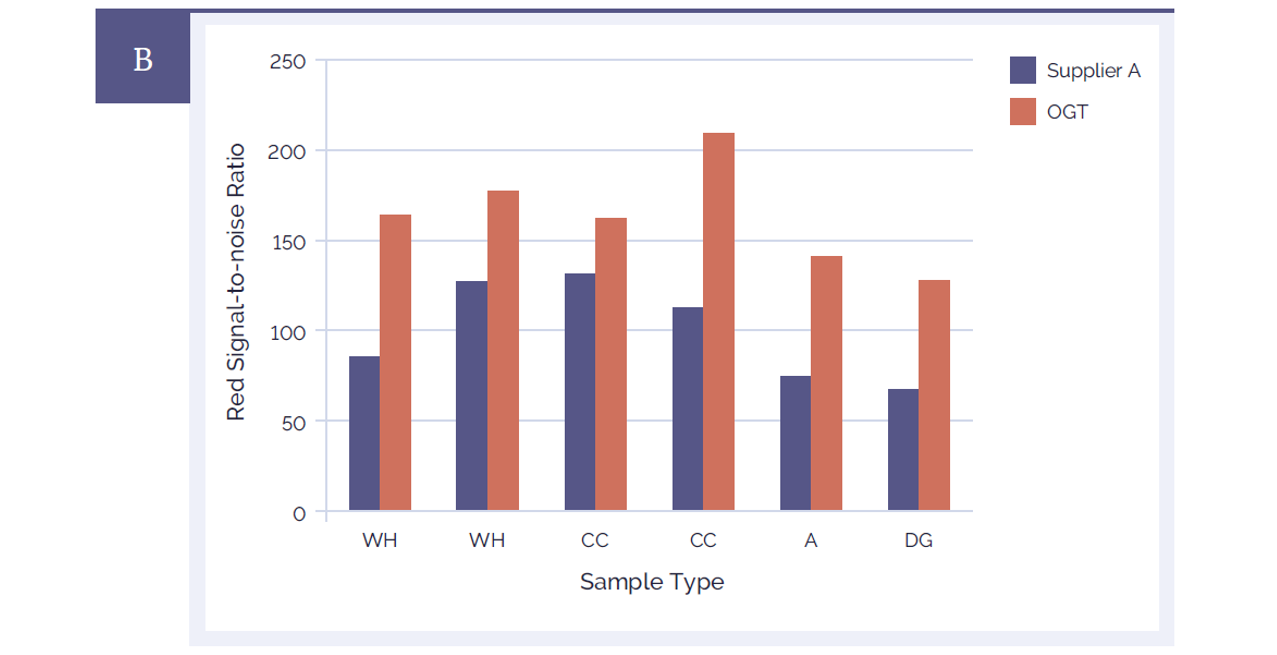
Figure 4B: CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits provide significantly improved signal-to-noise ratios than a leading alternative product. Using CytoSure ISCA v2 4x180k arrays the signal-to-noise ratios of 6 sample pairs labelled using the CytoSure Genomic HT DNA Labelling Kit (red bars) are compared against the signal-to-noise ratios obtained using a leading alternative kit (Supplier A) (blue bars). Panel A illustrates the green channel data, Panel B the red channel data. The CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kit delivered consistently higher signal-to-noise ratios than those obtained from Supplier A. The samples used were commercially available Coriell DNA (WH: WolfHirshhorn; CC: Cri du Chat; A: Anglemans; DG: Di George).

The excellent performance of CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits enables the reliable detection of aberrations and breakpoints, such as the deletions of varying sizes found in Wolf-Hirschhorn samples (Figure 5). Studies suggest that larger deletions tend to result in more severe intellectual disability and physical abnormalities than smaller deletions, so it is important to be able to determine breakpoints and gene content accurately. The identification of additional genes at the end of the short arm of chromosome 4 that contribute to the characteristic features of Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome will be important in understanding the genetic cause of this complex syndrome.
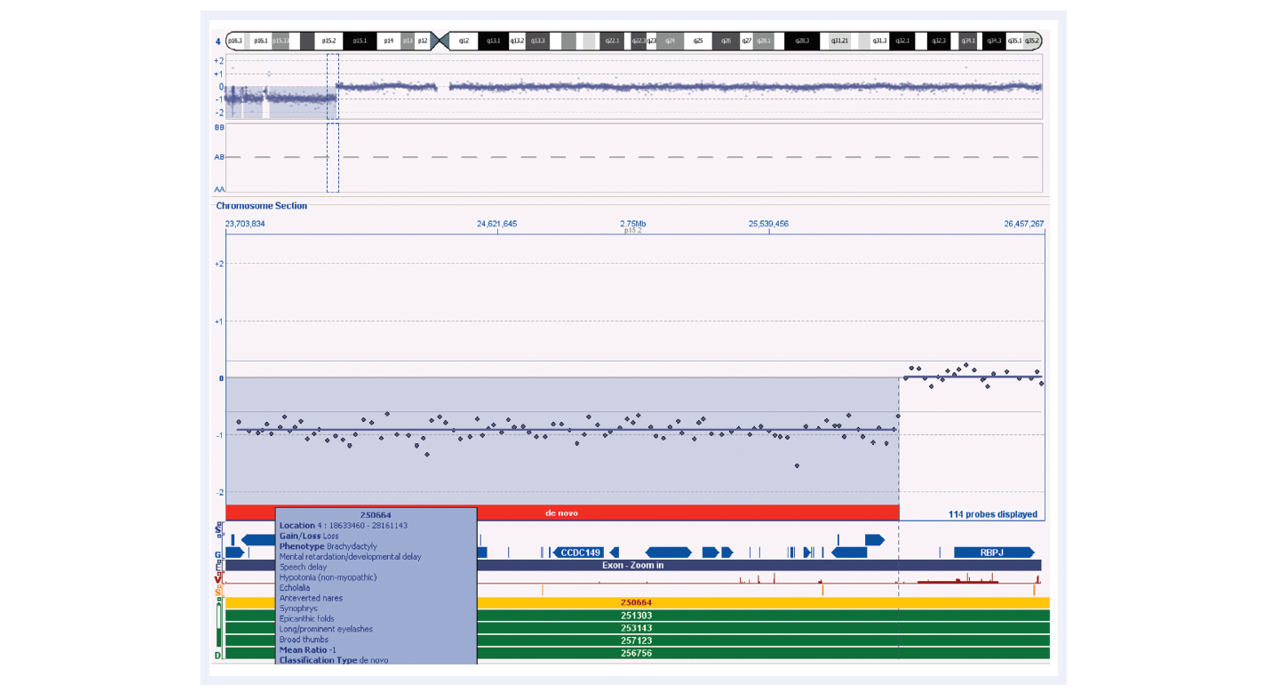
Figure 5: CytoSure Interpret Software in conjunction with the high-quality data obtained using CytoSure arrays and labelling kits allows accurate detection of chromosomal abnormalities. The loss on chromosome 4 for this Wolf-Hirschhorn sample contains many genes, as shown in the ‘Gene Track’. The low DLRS value enables accurate breakpoint determination. Using CytoSure Interpret Software, information regarding similar samples is easily accessible by simply highlighting the entry of interest in the DECIPHER track.

CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits offer faster and simpler DNA labelling and clean-up than alternative enzymatic labelling procedures, with improved data quality. The 24 reaction kit typically takes 5 hours from start to finish, while the 96 reaction kit takes around 6 hours (Figure 1). When using the high-throughput kit, the procedure can also be automated for implementation in high-throughput workflows. The simplified workflow does not compromise technical performance. OGT validation data generated and feedback from our customers demonstrates that using CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits improves DLRS values and signal-to-noise ratios ensuring accurate detection of even the smallest aberration.
A number of OGT customers have performed comprehensive DNA labelling kit evaluations prior to selecting CytoSure Genomic DNA Labelling Kits due to the consistently low DLRS values and excellent signal-to-noise ratios achieved. Reference customers are available on request.
CytoSure®: This product is provided under an agreement between Agilent Technologies, Inc. and OGT. The manufacture, use, sale or import of this product may be subject to one or more of U.S. patents, Pending applications, and corresponding international equivalents, owned by Agilent Technologies, Inc. The purchaser has the non-transferable right to use and consume the product for RESEARCH USE ONLY AND NOT for DIAGNOSTICS PROCEDURES. It is not intended for use, and should not be used, for the diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, treatment or alleviation of any disease or condition, or for the investigation of any physiological process, in any identifiable human, or for any other medical purpose.
Call +44 (0)1865 856800 Email contact@ogt.com
Send us a message and we will get back to you