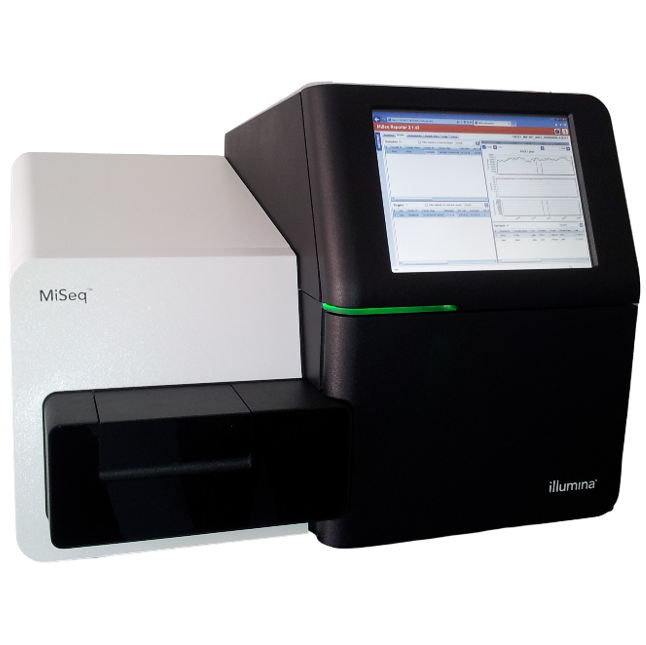
Although array comparative genomic hybridisation (aCGH) is still regarded as the gold standard for analysis of copy number variation (CNV) in intellectual disability (ID) and developmental delay (DD) research samples, it does not provide a comprehensive view of possible aberrations associated with a given sample. Additional assays such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) have to be performed in order to obtain critical insights such as the presence of causative single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and insertion/deletions (indels), with a subsequent increase in time and cost1.
There have been significant advances in sequencing technology and extensive developments in analysis software in recent years, but, up until now, NGS has not been able to robustly deliver single-exon CNV calling in a cost-effective manner and so has not been widely adopted in the cytogenetics research laboratory2.
The CytoSure® Constitutional NGS solution delivers CNV analysis down to single-exon level and loss of heterozygosity (LOH) as well as SNV and indel detection all in a single assay.
The CytoSure Constitutional NGS solution includes everything you have come to rely on with the well-established CytoSure microarray brand from OGT, namely, the most up-to-date ID/DD content, expert panel design, class-leading complimentary software and unparalleled support. It enables the seamless transition from microarrays to NGS, delivering a significant increase in information obtained from a single assay without extensive analysis time and costly data generation and storage.

Helping you to minimise analysis time

Everything you get from arrays and NGS in a single assay

Giving you the best chance to identify the aberration of interest

Robust single-exon CNV calling unlike other large targeted panels or exomes

Don’t spend time and effort sequencing, storing and analysing data that is not relevant
The NGS panel is designed to cover important genes for ID/DD and also contains a backbone of baits covering common single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), this allows detection of a comprehensive range of aberration types including CNVs, SNVs, indels and LOH in a single assay (Figure 1). This also includes detection within mosaic samples (Figure 2). The software user interface is conveniently arranged and also has the ability to switch between CNV/LOH calls and SNV/indel analysis, enabling a step-by-step approach to the interpretation process.
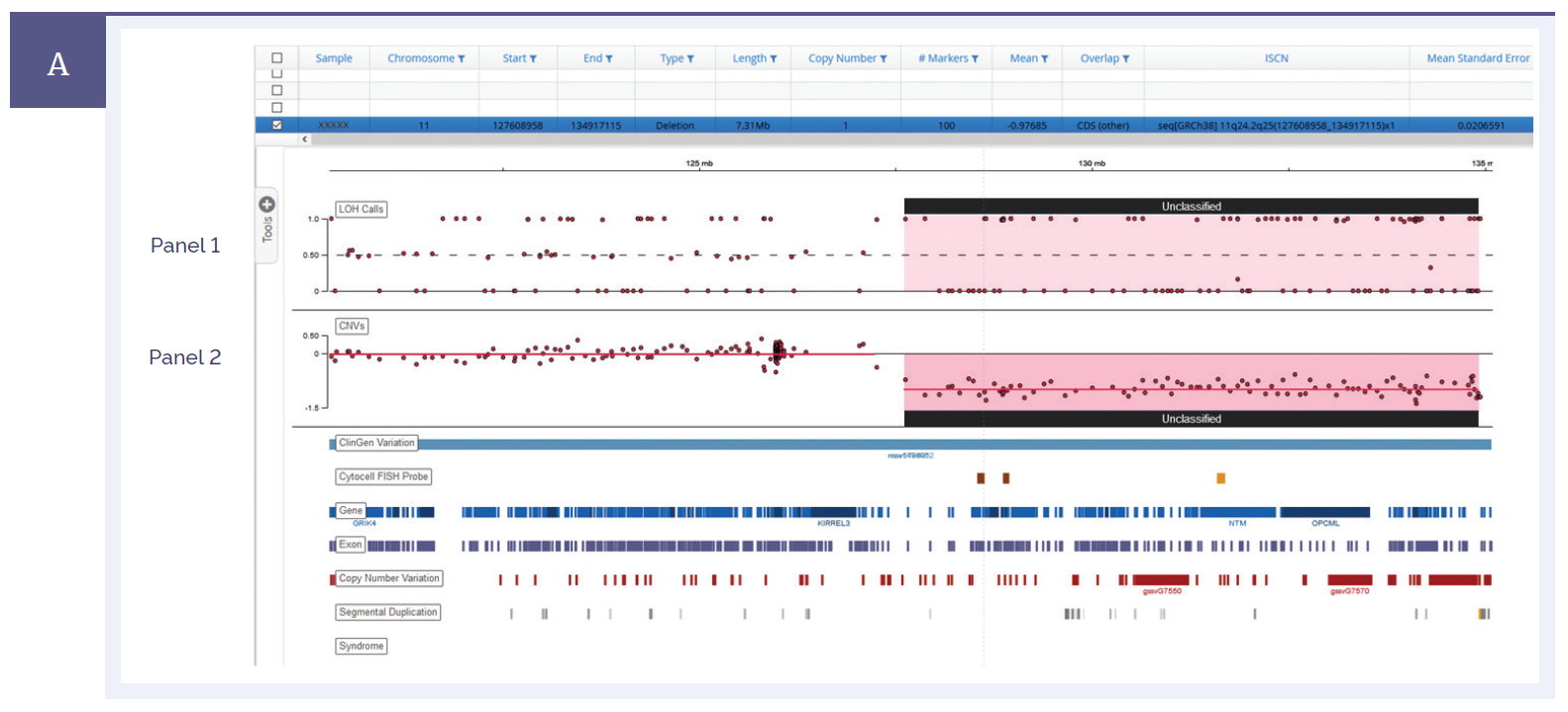
Figure 1a: A 7.3 Mb deletion detected on chromosome 11. Panel I shows the B allele frequency or LOH, whilst panel II shows the copy number ratio change*.

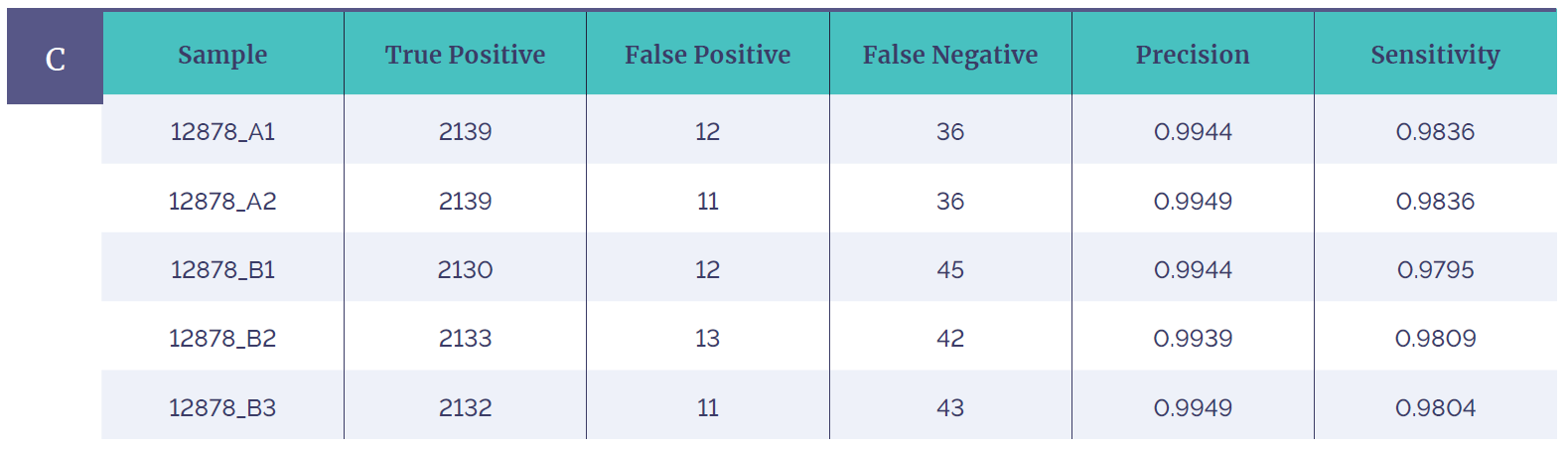
Figure 1c: Table shows reproducibility of 5 different runs of the Genome in a Bottle (GIAB) sample, the data demonstrates robust SNV detection achieved using the CytoSure Constitutional NGS Panel. Many of the false negatives fall in highly repetitive regions (e.g. homopolymer regions) and appear to be artifacts present in the GIAB WGS. These kinds of regions are highlighted in the software.

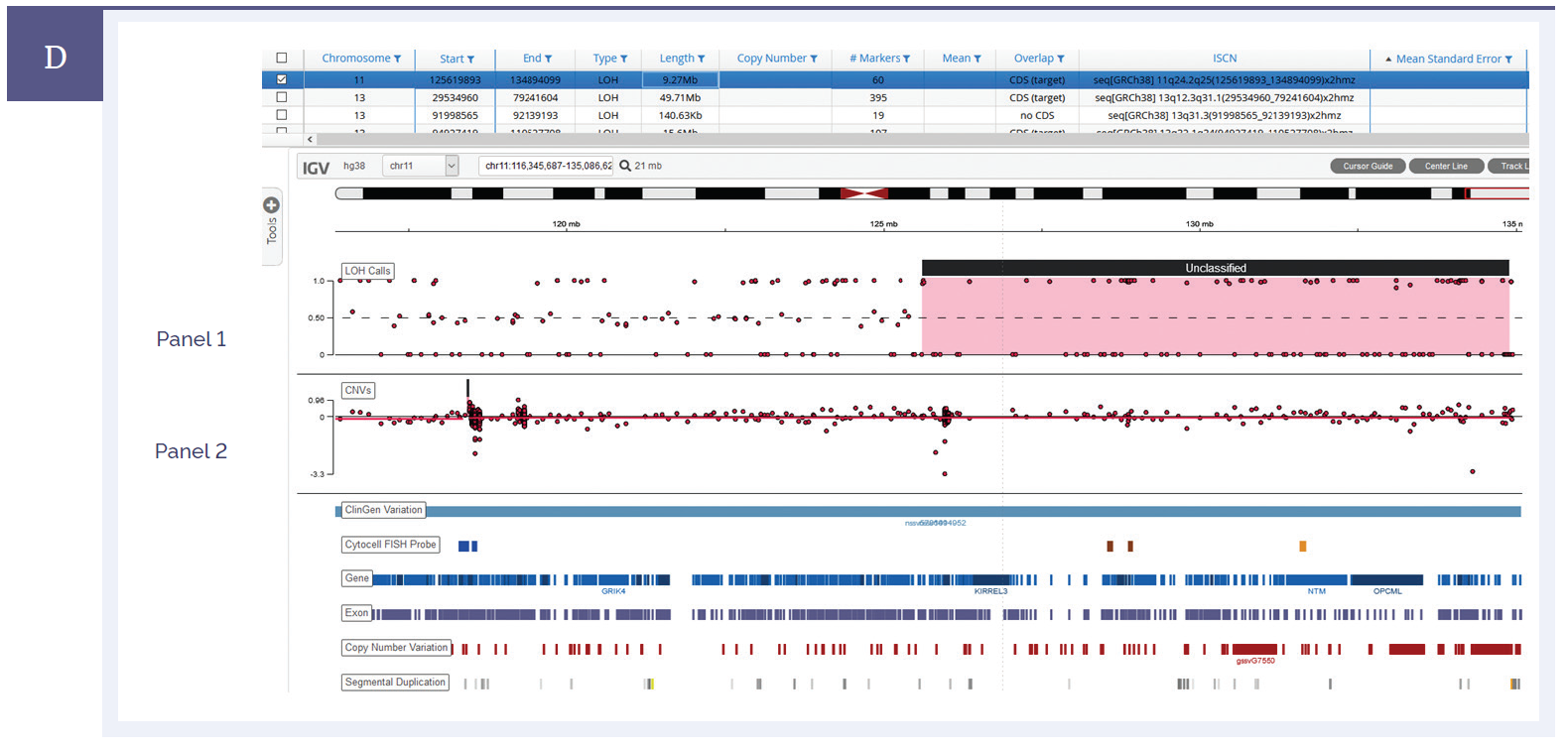
Figure 1d: A Consanguineous sample with a stretch of copy neutral LOH on chromosome 11. Panel I shows the B allele frequency whilst Panel II displays the copy number ratio.†

A key requirement in enabling the transition from a microarray-based technology to NGS for CNV detection is the ability to ensure that CNV data from the NGS panel is concordant with that from microarrays, particularly for small, sub-gene duplications and deletions. OGT’s expertise in bait design ensures uniform sequencing coverage of the desired regions. This, coupled with a proprietary CNV calling algorithm, allows robust detection of even the smallest CNVs (Figure 3).
It is important to ensure that the tools used in the laboratory are as up-to-date and comprehensive as possible. The CytoSure Constitutional NGS panel has been designed with input from leading experts in cytogenetics research as well as accessing information in international databases such as ClinGen3 and Deciphering Developmental Disorders (DDD)4.The panel contains over 700 targeted ID and DD genes including all exons and UTRs. Both the 5’ and 3’ UTRs are targeted in order to provide comprehensive coverage of the genes and to allow detection of any SNVs which may be relevant in these regions. The extensive set of backbone baits also enables detection of large CNV and LOH regions with a resolution of <5Mb (Figure 4).
View all CytoSure NGS content with our constitutional NGS chromosome search tool
One of the main challenges with exome or medical/clinical exome sequencing is the large amount of data generated per sample. This has obvious implications, not only on the cost to sequence individual samples at sufficient depth for robust variant calling, but also the costs and time associated with data storage and analysis. By focusing the panel on only the content required, it is possible to minimise costs for sequencing and data storage as well as analysis time. The ID/DD-focused content approach reduces the number of aberrations called compared to, for example, exome sequencing and, in particular, reduces the number of calls that would be classified as VUS, often requiring lengthy review and analysis.
The Interpret software offers standard variant and call attributes, which facilitate rapid data review (Figure 5), as well as numerous sophisticated filtering options (Table 1). The software also contains links to external databases for variant annotation.

* Clinical research sample provided courtesy of Centre hospitalier universitaire de Sherbrooke (CIUSSSE-CHUS). † Clinical research sample provided courtesy of EGL Genetics.